You go to the bathroom and notice your urine is foamy. A common misconception is that this is a sure sign of kidney disease. While foamy urine can sometimes indicate a kidney problem, it is not always the case. Many other, more common factors can cause your urine to appear bubbly or frothy. Understanding these other foamy urine causes can help you avoid unnecessary worry.
In this article, we will explain some of the other reasons why you might see foam in your urine and when you should actually be concerned.
Why Does Your Urine Get Foamy?
Foam is created when air gets trapped in a liquid. This can happen to your urine for a number of reasons, and many of them have nothing to do with your health.
1. Urination Speed and Force
A very simple and common reason for foam is the speed at which you urinate. If your bladder is full, your urine stream can be fast and forceful. This powerful stream hits the toilet water, stirring it up and creating temporary bubbles or foam, similar to pouring a liquid from a height into a glass. This type of foam usually disappears quickly, within a few minutes.
2. Cleaning Products in the Toilet
Sometimes, the foam you see is not from your urine at all. Residual cleaning chemicals or soaps left in the toilet bowl can react with your urine. This creates a soapy froth that can be easily mistaken for a medical issue. To check if this is the case, try urinating into a clean container and see if foam appears.
3. Dehydration
When you don’t drink enough water, your urine becomes more concentrated. It contains a higher ratio of waste products and proteins to water. This concentrated urine has a thicker consistency and can be darker in color. When it hits the toilet water, it is more likely to form a head of foam. Increasing your water intake is a simple solution if dehydration is one of your foamy urine causes.
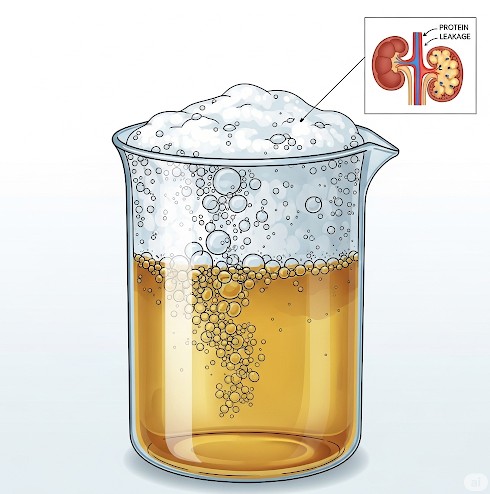
4. The Presence of Protein in Urine (Proteinuria)
This is the main cause that is sometimes linked to kidney disease. Healthy kidneys work as filters, keeping important proteins like albumin in your blood. However, when your kidneys are damaged, they may allow protein to leak into your urine. This condition is called proteinuria. The protein acts like a surfactant (similar to soap), reducing the surface tension of the urine and making it foamy.
5. Other Health Conditions
While not as common, some other health conditions can also contribute to foamy urine. For example:
- Diabetes: High blood sugar levels can damage the kidneys over time, leading to protein leakage.
- Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs): A UTI can cause inflammation, which may lead to a temporary increase of protein in the urine.
- Retrograde Ejaculation: In men, this condition causes semen to enter the bladder instead of being released, which can make the urine foamy.
When to See a Doctor
Seeing foam in your urine occasionally is usually not a cause for concern. However, you should see a doctor if:
- The foamy urine is persistent and happens often.
- The foam becomes more noticeable over time.
- You have other symptoms, such as swelling in your hands, feet, face, or abdomen.
- You also have other symptoms like fatigue, loss of appetite, or nausea.
A simple urine test can determine if you have a significant amount of protein in your urine. This can help your doctor find the actual foamy urine causes and recommend the right course of action.
References
- Healthline. (n.d.). Foamy Urine: Symptoms, Causes, and More. https://www.healthline.com/health/foamy-urine
- Cleveland Clinic. (n.d.). Foamy Urine: Bubbles, Causes, Diagnosis & What’s Normal. https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/symptoms/foamy-urine
- Medical News Today. (n.d.). Foamy urine: Causes and treatment. https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/322171